Volunteers distribute yard signs in June opposing a data center development in West Virginia.
ULYSSE BELLIER/AFP via Getty Images/AFP
hide caption
toggle caption
ULYSSE BELLIER/AFP via Getty Images/AFP
In Franklin, Indiana, Google recently sought approval to build an expansive campus dedicated to housing the servers that support its online services. However, the plan required rezoning over 450 acres in this Indianapolis suburb, sparking resistance from local residents.
Community members voiced concerns about the facility’s potential to consume vast quantities of water and electricity, while offering minimal advantages to the local economy. When a Google attorney announced at a public forum in September that the company was withdrawing its data center proposal, the crowd of sign-waving residents erupted in applause.
Across the United States, similar disputes are unfolding. On one hand, tech giants are investing billions into data centers designed to power artificial intelligence systems that could revolutionize daily life and work. On the other, communities worry about the environmental toll, rising energy costs, and the impact on their neighborhoods.
How policymakers and technology firms address these challenges will be pivotal in determining the trajectory of the AI sector in America and the nation’s global standing, experts in the field suggest.
Joseph Majkut, who leads the energy security and climate change program at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, highlights that local resistance could “delay industry growth or cause it to cluster unevenly across regions,” a factor often overlooked in discussions about AI expansion.
Below is an overview of the booming data center industry tied to AI and the critical issues it raises.
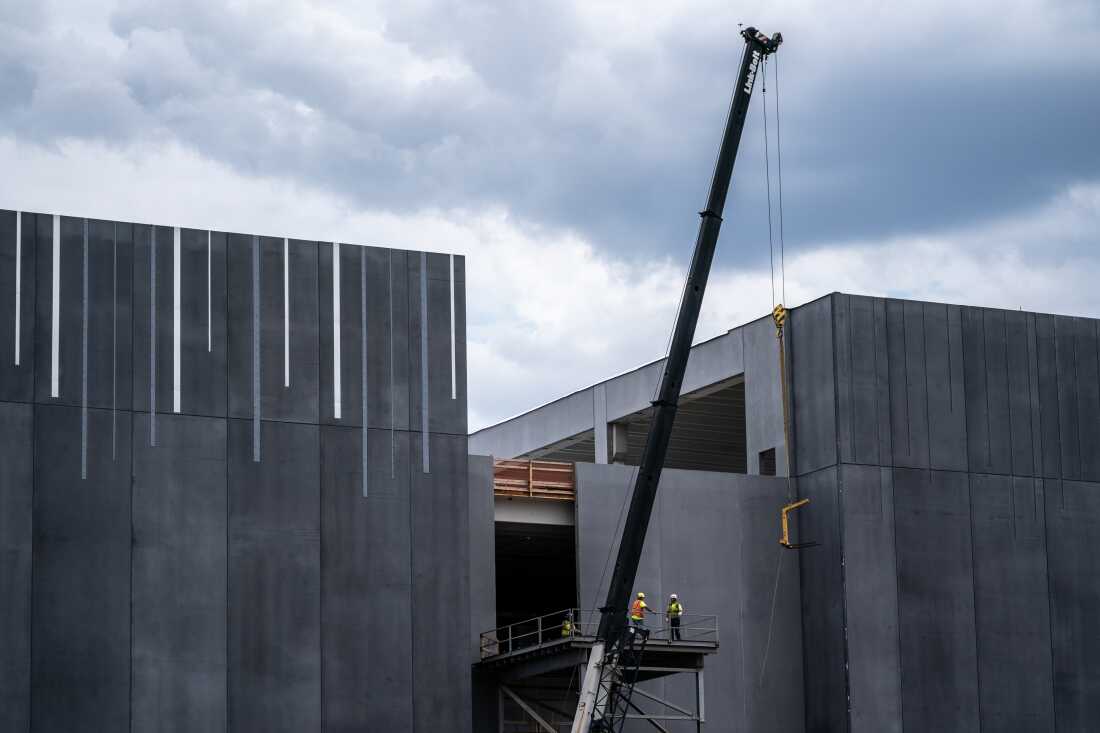

Construction workers erect a CloudHQ data center in Northern Virginia during 2024.
Nathan Howard/Getty Images/Getty Images North America
hide caption
toggle caption
Nathan Howard/Getty Images/Getty Images North America
Understanding Data Centers
Data centers are massive facilities that store and process digital data, serving as the internet’s critical infrastructure. Some of these centers span over a million square feet-equivalent to more than a dozen soccer fields.
Every time you browse a website, send an email, or make an online payment, data centers worldwide are at work behind the scenes.
However, this computing power comes with a significant environmental cost. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), a typical AI-focused data center consumes as much electricity as 100,000 homes, with the largest planned centers expected to use twenty times that amount. Additionally, these centers require billions of gallons of water annually to cool their equipment.
Why Are Data Centers in the Spotlight Now?
While data centers have existed for decades, the surge in AI investment has ignited a rapid expansion in their construction.
This growth is fueled by investors eager to capitalize on AI’s rising popularity among consumers and businesses alike. For instance, within two years of ChatGPT’s 2022 debut, nearly 40% of households in the U.S. and U.K. reported using AI chatbots, per the IEA. Similarly, the proportion of large companies employing AI jumped from 15% in 2020 to about 40% last year.
Tech firms are pouring hundreds of billions into data centers and AI-specific chips, anticipating increased adoption. Goldman Sachs projects that by 2027, AI will represent 28% of the global data center market-more than double its current share.
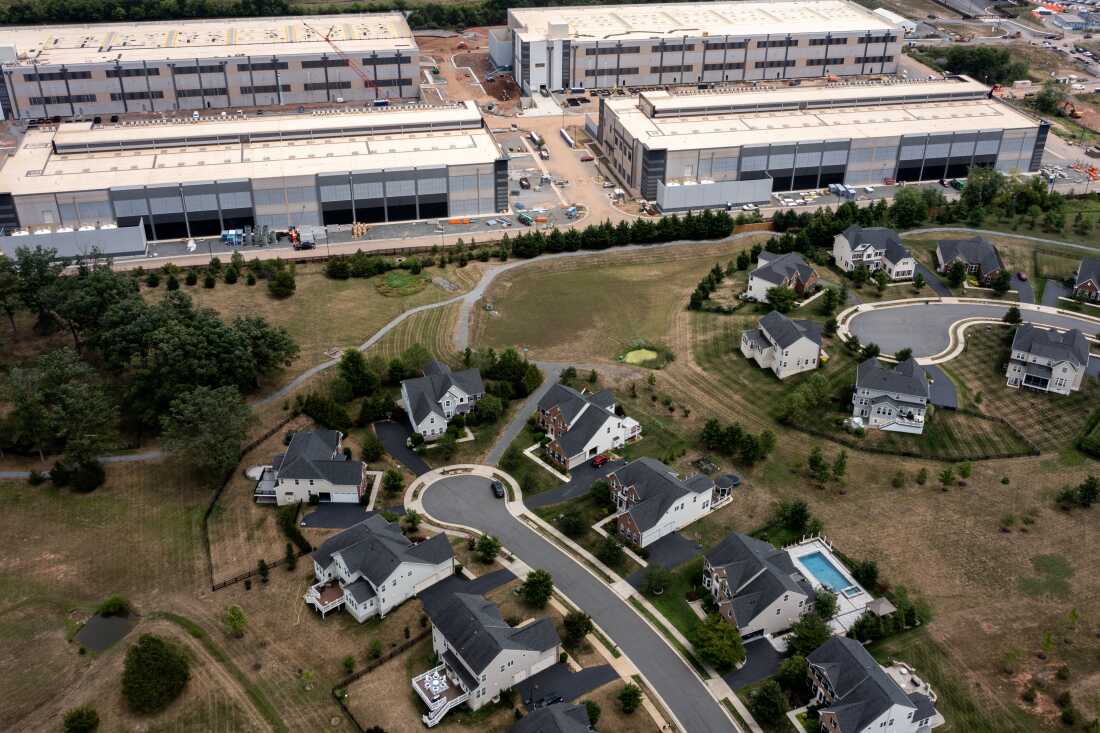

An Amazon Web Services data center located close to single-family residences in Stone Ridge, Virginia.
Nathan Howard/Getty Images/Getty Images North America
hide caption
toggle caption
Nathan Howard/Getty Images/Getty Images North America
Locations of Data Center Expansion
With substantial capital flowing in, developers are concentrating in established hubs like Northern Virginia’s renowned “Data Center Alley” and regions in Texas, as noted by the IEA. Yet, emerging markets such as Las Vegas are attracting attention due to affordable land, access to renewable energy, and tax incentives.
The Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis recently observed that a data center boom is just beginning within its jurisdiction, which includes Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, and parts of Michigan and Wisconsin.
Melissa Scanlan, director of the Center for Water Policy at the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, remarks, “We’re witnessing the initial stages of what these massive data center investments will look like on the ground.”
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence encompasses computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intellect, such as reasoning and decision-making, according to NASA.
AI applications range from generating digital art and videos to accelerating medical research by mapping protein structures for drug discovery. It also aids the energy sector in detecting pipeline leaks and managing power grids, and enhances weather forecasting accuracy.
To maintain a competitive edge, the U.S. must adapt to market demands, whether that means expanding AI-driven robotics or enhancing digital tools that boost professional productivity, explains Majkut. He also emphasizes the importance of American leadership in AI models and chip technology for national security and cybersecurity.
Hosting data centers domestically offers economic perks like construction employment and tax revenues, though some communities forgo a portion of these benefits through tax incentives aimed at attracting developers.
Andrew Chien, a computer science professor at the University of Chicago and senior scientist at Argonne National Laboratory, notes, “Because much of the initial investment is in physical infrastructure, having that capital flow domestically is a significant boon to the U.S. economy.” However, he cautions that communities must strategize to convert these investments into sustainable, well-paying jobs.
Since data centers require relatively few staff to operate, they typically do not generate many permanent employment opportunities once established.
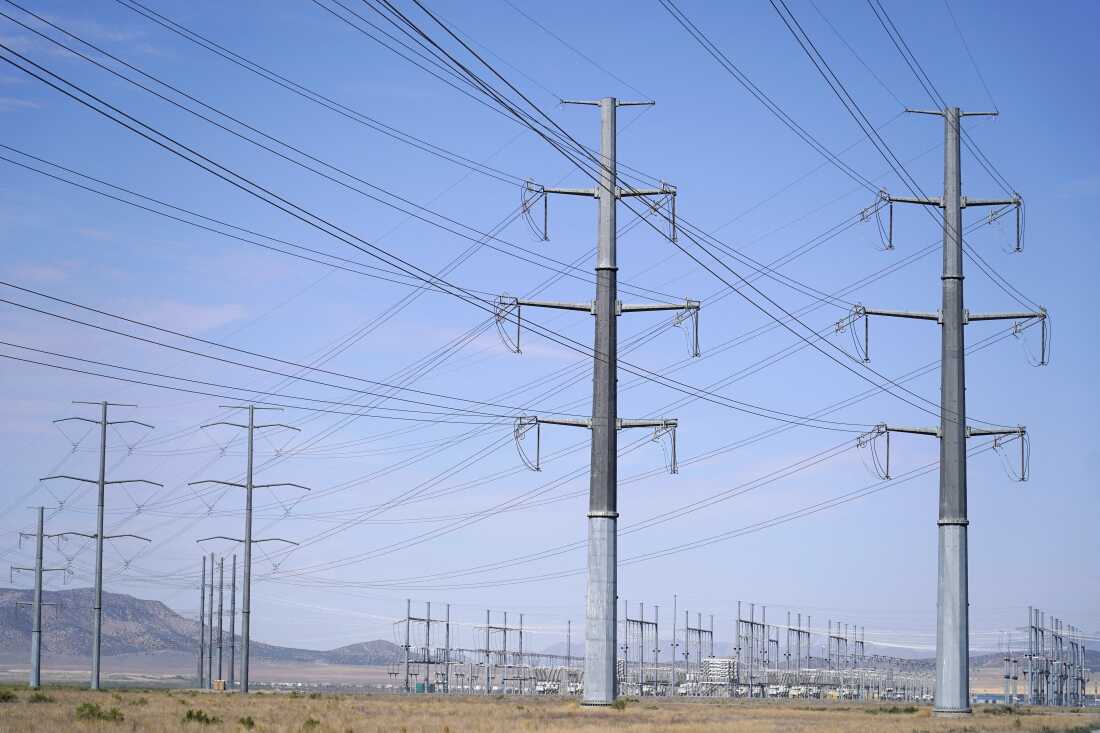

High-voltage transmission lines feed Meta’s Facebook data center in Eagle Mountain, Utah, a complex comprising five buildings each longer than four football fields, totaling 2.4 million square feet.
GEORGE FREY/AFP via Getty Images/AFP
hide caption
toggle caption
GEORGE FREY/AFP via Getty Images/AFP
Reasons Behind Community Resistance
Many residents oppose the introduction of large industrial complexes that alter the character of their neighborhoods through increased noise and light pollution.
Concerns also focus on the strain data centers place on local water resources for cooling, the potential rise in electricity costs, and the environmental impact if the centers rely on fossil fuel-generated power. The IEA warns that emissions from power plants serving data centers could more than double by 2035.
For example, in the Great Lakes region, which Scanlan describes as “a massive reservoir with multiple straws drawing water” from utilities, businesses, and power plants across eight U.S. states and two Canadian provinces, questions arise about the sustainability of increased water withdrawals for data centers and their energy suppliers.
In Georgia, some residents have reported diminished well water quality following the construction of nearby data centers. Similarly, certain Arizona municipalities have imposed limits on water deliveries to high-consumption facilities, including data centers.
Dan Diorio, vice president of state policy at the Data Center Coalition, an industry group, explains that companies are actively working to reduce water usage. While some centers use evaporative cooling that consumes water, others employ closed-loop systems that recycle water. For instance, a Google data center in Georgia utilizes treated wastewater for cooling and returns it to the Chattahoochee River. Efforts are also underway to develop cooling technologies that require no water.
“There’s a trade-off between water and electricity,” Diorio notes. “Using more electricity can reduce water consumption, and vice versa.”
Rising energy costs are another major issue, as data centers increase local power demand. A recent study by the Union of Concerned Scientists found that in 2024, residents and businesses in Illinois, Maryland, New Jersey, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia faced an extra $4.3 billion in electricity transmission costs linked to data center expansion.
Diorio emphasizes that the data center industry is committed to covering the full cost of electricity services.
It’s important to note that data centers are not the sole drivers of increased electricity demand; manufacturing facilities and the growing adoption of electric vehicles and appliances also contribute significantly.
Adding to public unease is the perception that tech companies lack transparency about their water and energy consumption, making it difficult for communities to make informed decisions about new data center projects.
Diorio acknowledges that while companies strive to be responsible community partners, they sometimes hesitate to disclose operational details due to competitive concerns.
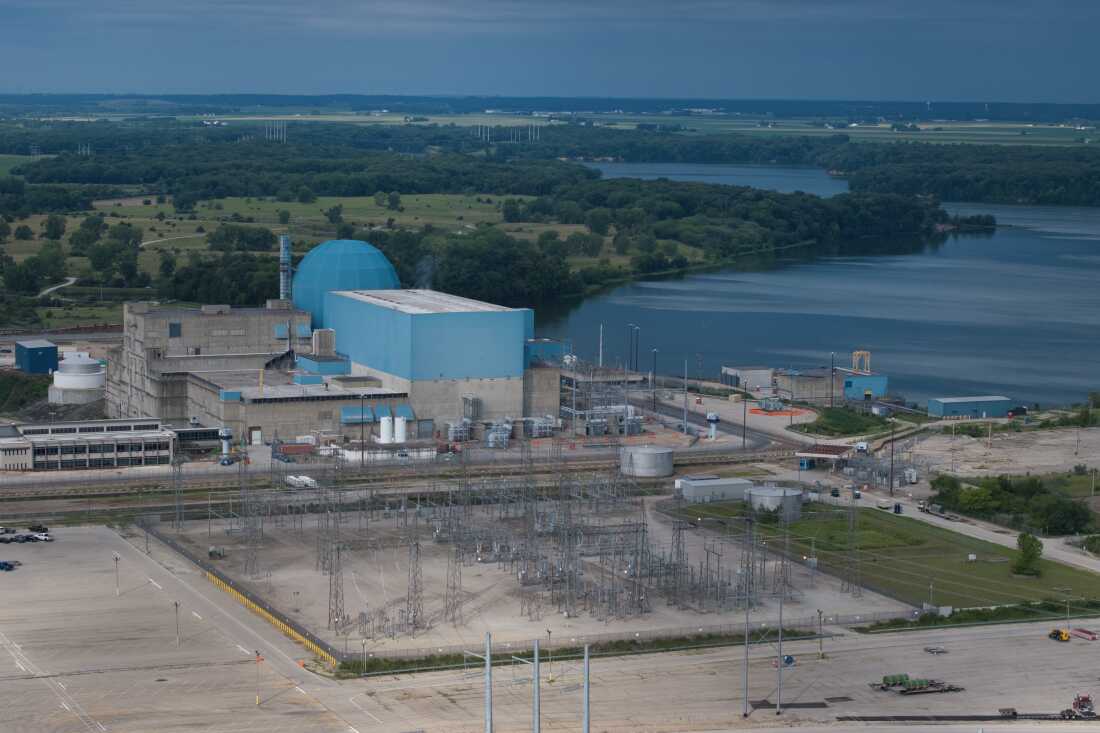

An aerial shot of Constellation’s Clinton Clean Energy Center nuclear power plant in Illinois. Meta recently secured a 20-year power purchase agreement with Constellation for this plant’s output.
Scott Olson/Getty Images/Getty Images North America
hide caption
toggle caption
Scott Olson/Getty Images/Getty Images North America
Additional Obstacles to Data Center Growth
The foremost challenge is securing sufficient electricity to meet escalating demand.
During the Trump administration, efforts were made to restrict renewable energy projects. Industry leaders and analysts argue that renewables are essential for rapidly expanding power capacity because they can be deployed quickly and offer relatively low-cost electricity.
Pavan Venkatakrishnan, an infrastructure fellow at the Institute for Progress, points out a “clear contradiction” between the administration’s stance on renewables and its ambition to accelerate data center development.
White House spokesperson Kush Desai stated that AI “cannot depend on unreliable energy sources that require heavy subsidies to be cost-effective. The administration prioritizes unleashing energy forms like natural gas and nuclear that function effectively without ongoing government support, powering America’s next Golden Age.”
While solar and wind power combined with battery storage are reliable energy options, experts agree that natural gas and nuclear energy will also be vital in meeting new electricity needs. However, these technologies currently cannot be scaled up quickly enough to satisfy immediate demand.